Background: Myelodysplastic neoplasms (MDS) and acute myeloid leukemia (AML) with multi-hit TP53 comprise the highest risk subgroup of all myeloid malignancies. TP53 aberration is recognized as a diagnostic category in the 2022 International Consensus Classification (ICC) and the 5 th edition of the WHO. However, these systems do not discern among the subtypes of TP53 aberrations regarding response to therapy. In this study, we explore the clonal dynamics that underlie such prognostic heterogeneity within distinct subgroups of TP53-aberrant MDS and AML, with a specific focus on the effect of hypomethylating agent (HMA) vs. araC-based chemotherapy on TP53 variant allele frequency (VAF).
Methods: The UMass Leukemia Registry from the UMass Data Lake identified 76 patients harboring TP53 aberration(s) plus ICD-10 code of either D46.9 (MDS and its subentities) or C92.00 (AML and its subentities) between 2011-2023. Data was integrated with hematopathology records. TP53 exome sequencing was performed with coverage depth 500X to 6500X, and VAFs were adjusted for copy number variation (CNV), as previously described (Patel SA et al., Leuk Lymphoma 2021; 62: 3348-60). Patients with serial bone marrow biopsy samples were included. We defined multi-hit TP53 status as per the ICC: two or more distinct TP53 mutations with VAF ≥ 10%, or a single TP53 mutation plus one of the following abnormalities: (1) del(17p13.1), (2) TP53 VAF >50%, (3) copy-neutral loss-of-heterozygosity, or (4) any complex karyotype. Clonal dynamics were assessed for MDS vs. AML and for varying TP53 allelic states as a function of therapeutic intervention. Clinical fate mapping was performed based on management decisions at various points of clinical care.
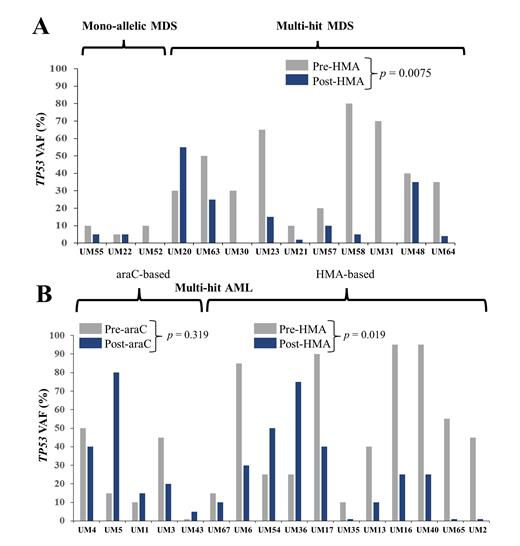
Results: For patients with TP53-aberrant MDS, 17 patients underwent serial bone marrow biopsies during treatment. Of these, 11 (64.7%) had multi-hit status. Eight patients (47.1%) underwent hematopoietic cell transplant (HCT), and 7 of these 8 patients had received HMA-based front-line therapy. For patients with MDS, we assessed the effect of HMA-based therapy on TP53 VAF. The mean TP53 VAF (sum of VAFs) was significantly lower after HMA-based treatment (35% vs. 12.6%) ( p = 0.0075) (Panel A). For patients with TP53-aberrant AML, 19 patients underwent serial bone marrow biopsies. Of these, 14 (73.7%) had multi-hit status. Only 2 patients (10.5%) underwent HCT. Five patients (26.3%) received araC-based induction, while 11 patients (57.9%) initially received HMA-based induction. For patients with AML with multi-hit TP53, we assessed the effect of HMA-based vs. araC-based front-line therapy on TP53 VAF. HMA therapy led to mean fold reduction in TP53 VAF (pre-treatment to post-treatment) of 11.7 ± 5.8 ( p = 0.019), while araC-based therapy actually led to mean fold increase (but not statistically significant) in TP53 VAF (pre-treatment to post-treatment) of 2.6 ± 1.05 ( p = 0.319) (Panel B). HMA-based treatment resulted in significantly greater reduction in the VAF in aberrant clones and subclones compared to araC-based treatment. Compared to AML, most patients with MDS (62.9%) proceeded with palliative intent therapy at the time of diagnosis. Although patients with AML (53.7%) attempted to proceed with curative intent at the time of diagnosis, only 14.6% eventually proceeded with HCT, largely due to clinical decompensation or disease progression during front-line therapy. Among HCT recipients for MDS ( n =10), 7 (70%) remained in remission. Among HCT recipients for AML (n = 6), 4 (66.7%) remained in morphologic leukemia-free state.
Conclusion: There is limited literature on clonal and subclonal diversity in patients with MDS or AML with TP53 aberrations. Such considerations constitute an important therapeutic issue, as certain interventions may only eliminate a fraction of a patient's mutant cells. In our study, HMA- and araC-based regimens had differential effects on various subclones: HMA was more effective in reducing the TP53 mutational burden and increasing patient ability to proceed with HCT. AraC-based therapy appeared less effective, perhaps due to selection pressure in favor of TP53-mutant cells. Prospective trials are required to identify optimal regimens that lead to the best long-term outcomes, and single-cell resolution might assist with more definitively assessing dynamics of clonal response to treatment.
Disclosures
Patel:UMass Center for Clinical and Translational Science (CCTS) Pilot Project Program grant (NIH / NCATS Grant UL1TR001453: Research Funding; Bristol Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pfizer: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Cerny:MERIT CRO: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Actinium Pharmaceuticals: Current holder of stock options in a privately-held company; BlueBird Bio, Inc: Current holder of stock options in a privately-held company; Cellectar Sciences: Current holder of stock options in a privately-held company; Dynavax Technologies: Current holder of stock options in a privately-held company; Gamida Cell: Current holder of stock options in a privately-held company; Atyr Pharma: Current holder of stock options in a privately-held company; Novavax Inc: Current holder of stock options in a privately-held company; Ovid Therapeutics Inc: Current holder of stock options in a privately-held company; Sorreto Therapeutics: Current holder of stock options in a privately-held company; Veru Inc: Current holder of stock options in a privately-held company; Viridian Therapeutics: Current holder of stock options in a privately-held company; Vaxart Inc: Current holder of stock options in a privately-held company; 2Seventy Bio Reg SHS: Current holder of stock options in a privately-held company; Bristol Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; ICON- Prolacta: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; ICON- Allovir: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Gerber:AbbVie: Divested equity in a private or publicly-traded company in the past 24 months; Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding; Hutchmed: Research Funding; Bristol Myers Squibb: Research Funding; Stemline Therapeutics, Inc.: Research Funding.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal